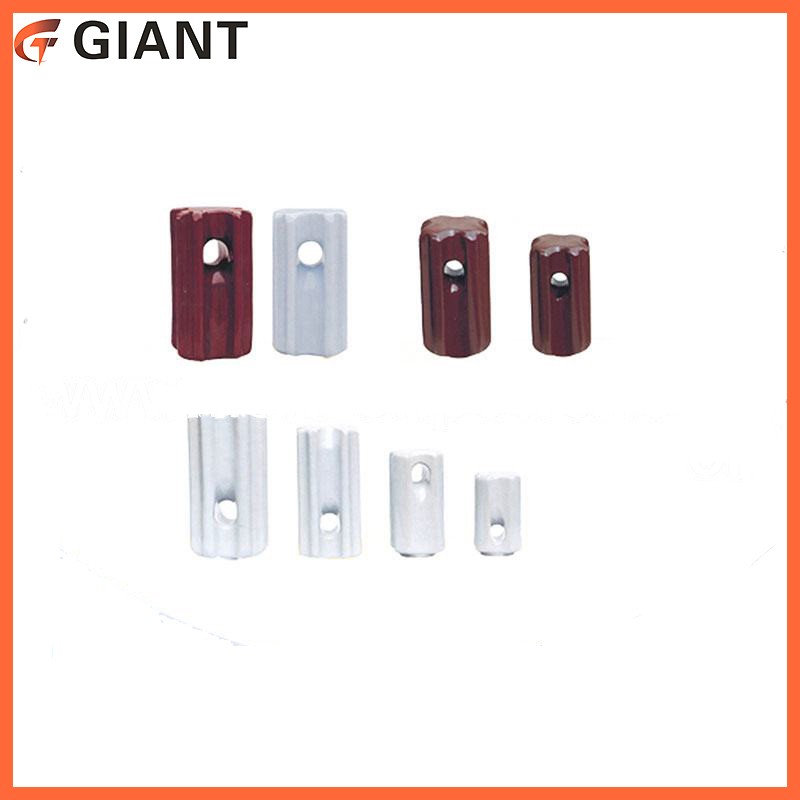
An insulator is a material or method that restricts the transfer of either heat or electricity. In the case of heat, thermal insulators work by reducing the rate heat can travel through a space. Generally, they use specific materials and will keep heat-carrying matter from moving. In the case of electricity, electrical insulators confine an electric current to a designated path. They typically work by using a material with many outer elections, a condition that will cause lowelectrical conductivity.
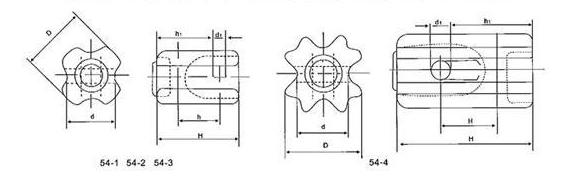
| Type | GY1 | GY2 | GY3 | GY4 | 54-1 | 54-2 | 54-3 | 54-4 |
| Creepage Distance mm |
|
|
|
|
41 | 48 | 57 | 76 |
| main dimension(H) | 90 | 146 | 216 | 280 | 89 | 108 | 140 | 171 |
| main dimension(h) | 48 | 73 | 89 | 89 | 44 | 57 | 79 | 67 |
| main dimension(h) | 60 | 99 | 133 | 165 | 64 | 76 | 103 | 114 |
| main dimension(O) | 68 | 73 | 115 | 115 | 64 | 73 | 86 | 89 |
| main dimension(d) | 10 | 44 | 67 | 67 | 44 | 54 | 60 | 60 |
| main dimension(d1) | 16 | 22 | 38 | 38 | 16 | 22 | 25 | 25 |
| Mechanical Falling Load KN | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 44 | 53 | 89 | 89 |
| Power frequency flashower voltage dry/kv | 27 | 71 | 222 | 222 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 |
| Power frequency flashower voltage Wet/kv |
|
|
|
|
12 | 15 | 18 | 23 |
| Apply Standard | AS | ANSI | ||||||